Binomial Distribution
BINP
B = Binary process = 2 process
I = Independent event
N = Number of trials
P = Probability of success
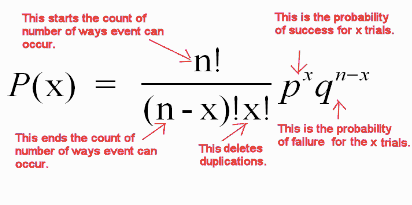
Binomial Probability
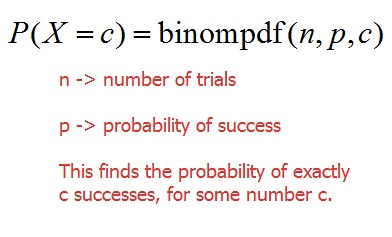
binompdf(n, p, x)
n=trials
p=probability
x=value
Calculator
- 2ND + VARS (DISTR)
A: binompdf / B: binomcdf
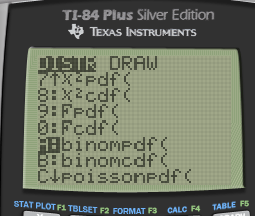
binompdf vs binomcdf

Practice Questions for Binomial Distribution
A manufacturer produces a large number of toasters. From past experience, the manufacturer knows that approximately 4% are defective. In a quality control procedure, we randomly select 40 toasters for testing.
- Determine the probability that exactly one of the toasters is defective
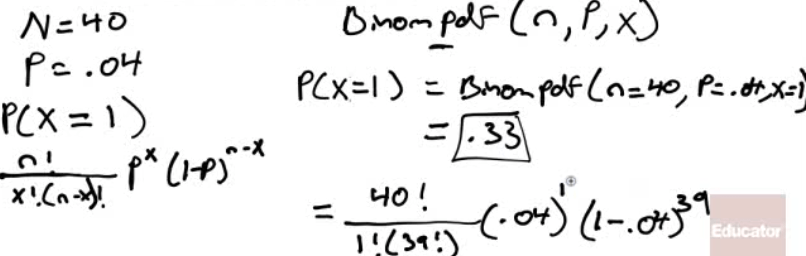
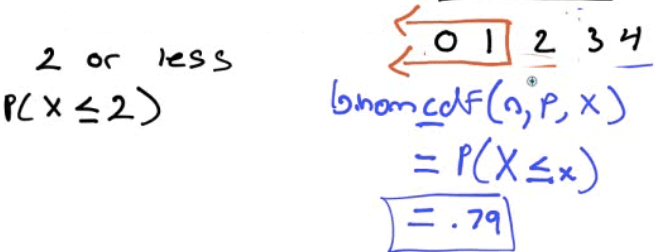
Find the probability that at most two of the toasters are defective
Find the probability that more than three toasters are defective
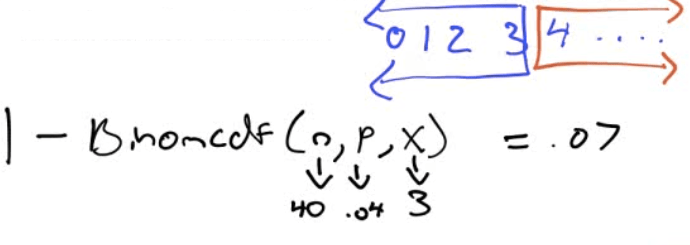
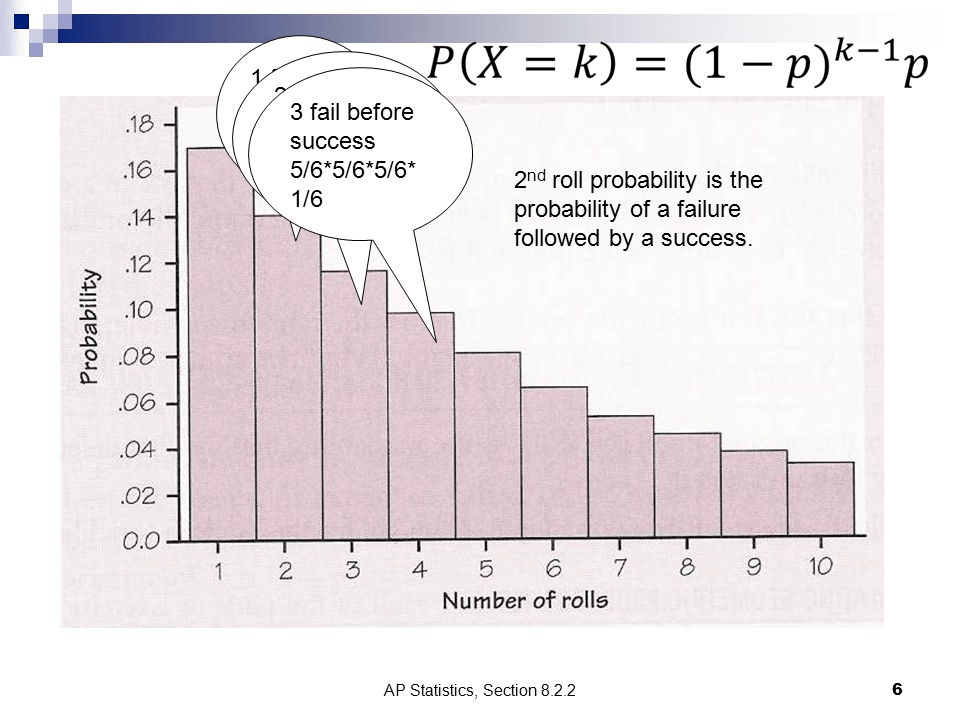
Geometric Distribution
BI
NP- Not given the number of trials
Question Format
- How many trials until a success
Geometric Probability
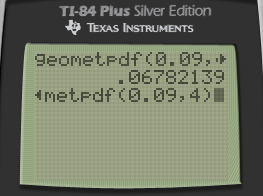
geometpdf(p,x)
geometcdf(p,x)
p=probability of success
x=number of trials until 1 success
Practice Questions for Geometric Distribution
There is a probability of 0.09 that a vaccine will cause a certain side effect. Suppose that a number of patients are inoculated with the vaccine. We are interested in the number of patients vaccinated until the first side effect is observed
- Find the probability that exactly 4 patients must be vaccinated in order to observe the first side effect.
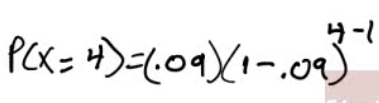
What is the probability that the number of patients vaccinated until the first side effect is observed at most 5?
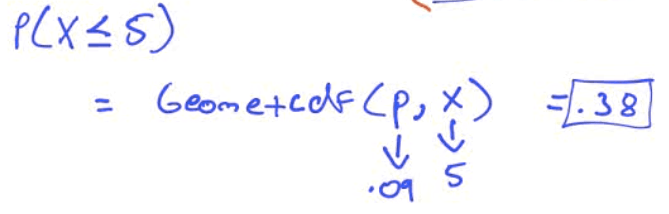
Mean and Standard Deviation
